Experiments with vision transformers ←
Classifying FMNIST ←
Using the torchvision.models.VisionTransformer on the FMNIST dataset,
with torchvision.transforms.TrivialAugmentWide data augmentation.
Training is done for 2M steps which translates to ~32 passes through the training set.
The training (and validation) loss is the l2 distance between the FMNIST class (10 numbers, either 0 or 1) and the network output.
There is an additional layer (of size cs) before the classification layer
that is used as embedding. During validation, a Support Vector Classifier
(sklearn.svm.SVC with default parameters) is fitted to the embedding/labels to see
if the embedding contains enough information to classify the images in
a non-NN fashion (accuracy (svc)). Also the torch.argmax is
compared between FMNIST class logits and network output (accuracy (argmax))
to measure the accuracy of the true network output.
matrix:
patch: [7] # transformer input patch size
layer: [8] # number of layers
head: [16] # number of attention heads
hidden: [256] # size of hidden dimension
mlp: [512] # size of hidden dimension in MLP stage
drop: [0.] # MLP dropout
cs: [784] # size of code before classification layer
experiment_name: aug/fmnist_vit_trivaug_${matrix_slug}
train_set: |
ClassLogitsDataset(
fmnist_dataset(train=True, shape=SHAPE),
num_classes=CLASSES, tuple_position=1, label_to_index=True,
)
validation_set: |
ClassLogitsDataset(
fmnist_dataset(train=False, shape=SHAPE),
num_classes=CLASSES, tuple_position=1, label_to_index=True,
)
trainer: experiments.reptrainer.RepresentationClassTrainer
batch_size: 64
learnrate: 0.0003
optimizer: AdamW
scheduler: CosineAnnealingLR
loss_function: l2
max_inputs: 2_000_000
train_input_transforms: |
[
lambda x: (x * 255).to(torch.uint8),
VT.TrivialAugmentWide(),
lambda x: x.to(torch.float32) / 255.,
]
globals:
SHAPE: (3, 28, 28)
CODE_SIZE: ${cs}
CLASSES: 10
model: |
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
from torchvision.models import VisionTransformer
self.encoder = VisionTransformer(
image_size=SHAPE[-1],
patch_size=${patch},
num_layers=${layer},
num_heads=${head},
hidden_dim=${hidden},
mlp_dim=${mlp},
num_classes=CODE_SIZE,
dropout=${drop},
)
self.linear = nn.Linear(CODE_SIZE, CLASSES)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(self.encoder(x))
Encoder()
I varied a few parameters of the transformer without significant change to the downstream accuracy, except, of course, that a much bigger network performs much worse (like in previous experiments).
For comparison there is included an untrained ResNet18 (RN18) and a simple
ConvEncoder (CNN, ks=3, channels=(32, 32, 32), ReLU, output=128).
| model | patch | layer | head | hidden | mlp | drop | cs | validation loss (2,000,000 steps) | accuracy (argmax) | accuracy (svc) | model params |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RN18 (white) | 128 | 0.01189 | 0.9206 | 0.9237 | 11,243,466 | ||||||
| ViT (grey) | 7 | 4 | 16 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01429 | 0.9063 | 0.9076 | 2,185,610 |
| ViT (purple) | 7 | 4 | 8 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01460 | 0.9034 | 0.9042 | 2,185,610 |
| ViT (not shown) | 7 | 4 | 32 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01482 | 0.9025 | 0.9013 | 2,185,610 |
| ViT (orange) | 7 | 8 | 8 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01499 | 0.8992 | 0.9014 | 4,294,026 |
| ViT (yellow) | 7 | 8 | 16 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01514 | 0.8997 | 0.9003 | 4,294,026 |
| ViT (magenta) | 7 | 8 | 16 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 784 | 0.01518 | 0.8993 | 0.9009 | 4,469,178 |
| ViT (red) | 7 | 8 | 8 | 256 | 1024 | 0 | 128 | 0.01526 | 0.9002 | 0.9019 | 6,395,274 |
| ViT (blue) | 7 | 4 | 4 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.01529 | 0.8958 | 0.8980 | 2,185,610 |
| ViT (green) | 7 | 16 | 8 | 256 | 512 | 0 | 128 | (780,000 steps) 0.01897 | 0.8665 | 0.8728 | 8,510,858 |
| CNN (light green) | 128 | 0.01962 | 0.9086 | 0.9181 | 2,002,698 | ||||||
| ViT (dark blue) | 7 | 8 | 12 | 768 | 512 | 0 | 128 | 0.02125 | 0.8477 | 0.8502 | 25,453,962 |
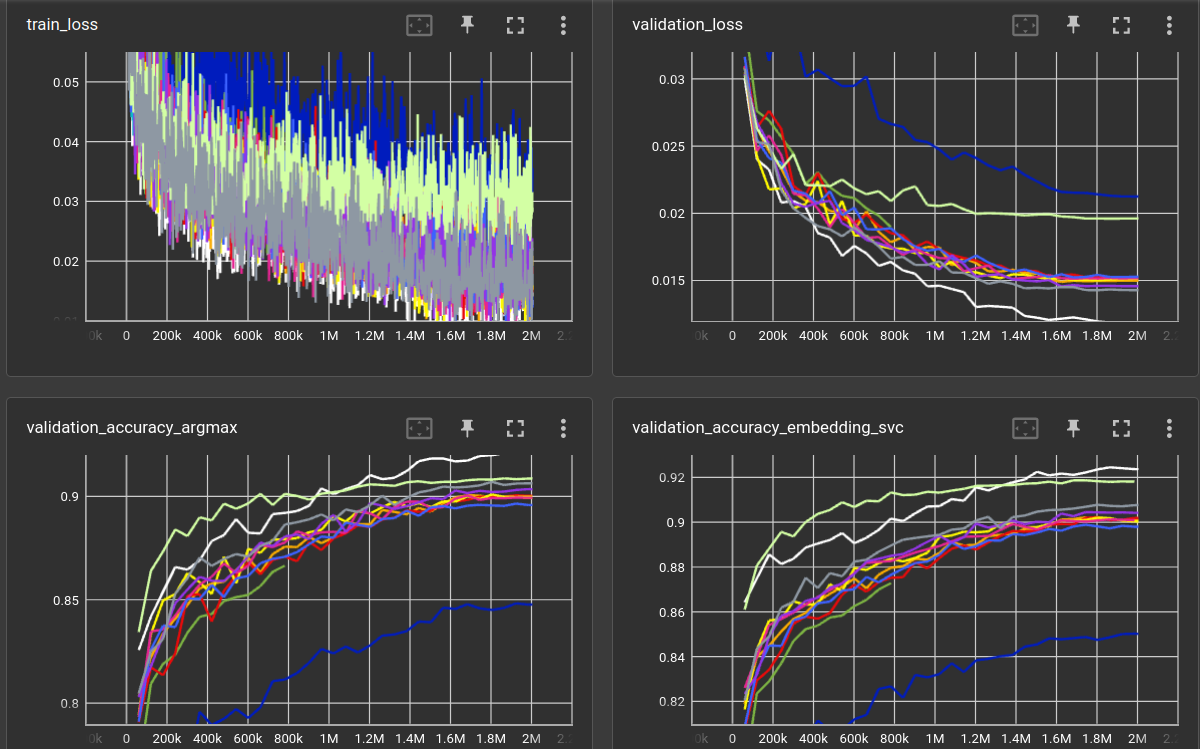
Noteable things:
TrivialAugmentWidecreates quite some training loss noise ;)- Despite the bad validation loss (l2 distance of class logits), the CNN has comparatively good accuracy
- Generally, the validation loss does not entirely correlate with the classification accuracy
- And, of course, i obviously don't know how to train Transformers. The ResNet beats them all! It is very likely that 30 epochs are too short to even see a difference between the different Transformer sizes. They all seem to converge at roughly the same place after 2M steps, with a little trend: smaller is better :facepalm:
- The SVC accuracy is always (very slightly) higher than the argmax accuracy. One can probably assume that a Support Vector Machine is more powerful than a single linear NN layer.